How to Become a Sterile Processing Technician
A sterile processing technician, also known as a CSSD technician or sterilization supply tech, is an important member of the healthcare team. Sterile processing technicians are responsible for the very important task of sterilizing surgical instruments and supplies. This job is essential for ensuring that surgeries are performed in a safe and clean environment.
Sterile processing technicians typically work in hospitals or other healthcare facilities. As a sterile processing technician, you will be responsible for cleaning, disinfecting, and sterilizing surgical instruments and other medical equipment.
A career as a sterile processing technician can be very rewarding. Aside from making sure that medical equipment are clean and safe to use, sterile processing technicians also maintain records of sterilization procedures, stocking surgical supply rooms, and assembling surgical kits.
In order to perform their job effectively, sterile processing technicians must have excellent attention to detail and be able to follow instructions carefully.
In this blog post, we will give you an overview of what you need to do to become a sterile processing technician.
Education and Training Requirements
Most sterile processing technicians have at least a high school diploma or equivalent, although some positions may require postsecondary education or certification.
Many community colleges offer certificate or associate degree programs in sterile processing and related fields such as health science or medical laboratory technology.
These programs typically take one to two years to complete and include coursework in microbiology, anatomy, and physiology. Some states require sterile processing technicians to be licensed or certified.
The education and training requirements for becoming a sterile processing technician vary by state, but most states require that sterile processing technicians complete an accredited Sterile Processing Technician program.
These programs usually last between 9 and 12 months and culminate in a certificate or diploma. Some states also require certification from the Certification Board for Sterile Processing and Distribution (CBSPD) or the International Association of Healthcare Central Service Materiel Management (IAHCSMM).
In addition to completing an accredited program and obtaining certification, most employers also require some on-the-job training. On-the-job training usually lasts between 4 and 6 weeks.
During on-the-job training, new sterile processing technicians learn how to use the specific equipment and products used by their employer. They also learn about their employer’s specific policies and procedures related to sterilization.
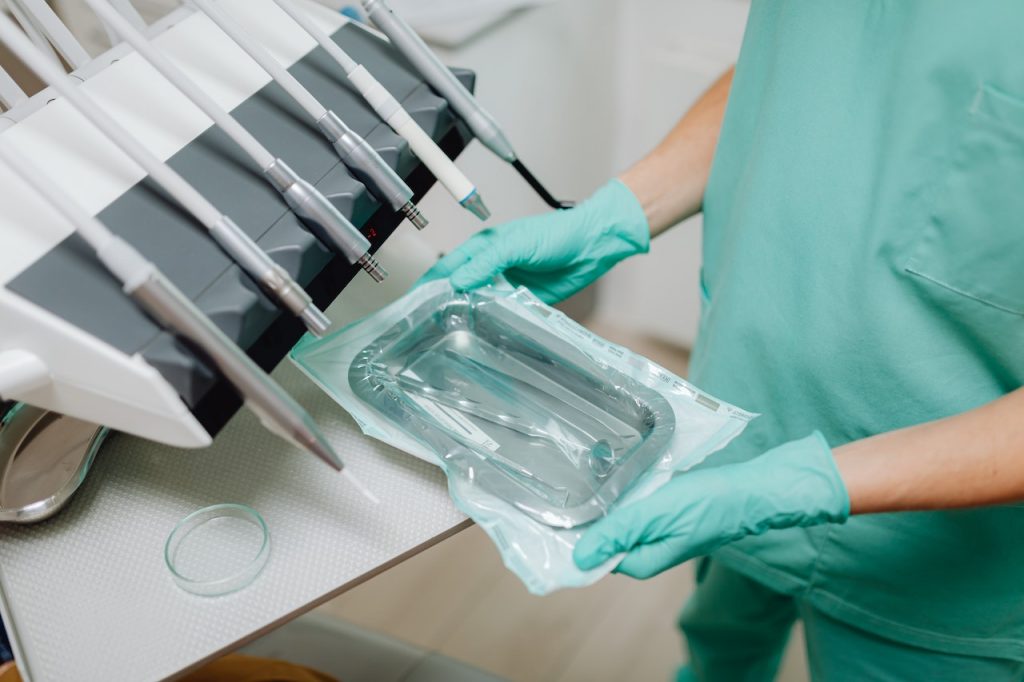

Skills Required
In addition to the specific education and training requirements discussed above, there are several skills that are required for being successful as a sterile processing technician.
Strong attention to detail is essential for this job because even the smallest mistake can have serious consequences. Sterile processing technicians must also be able to follow instructions carefully in order to ensure that instruments are properly sterilized.
Other important skills for sterile processing technicians include good communication skills, physical stamina, manual dexterity, and good organizational skills.
Sterile processing technicians must also be able to follow instructions carefully and work well under pressure.
Overall, sterile processing technicians have a very important job. If you are detail oriented and have good communication and organizational skills, then a career as a sterile processing technician may be a good fit for you.
Working Conditions
Sterile processing technicians typically work in hospitals or other healthcare facilities. They may work full time or part time, and their schedules may vary depending on the needs of their employer.
Some sterile processing technicians may be required to work evenings, weekends, or holidays. Overtime may also be required on occasion.
Sterile processing technicians typically work in well-lit and ventilated areas. However, they may be exposed to unpleasant odors and chemicals. They may also be required to lift and move heavy objects.
Sterile processing technicians may be exposed to infectious diseases and hazardous materials; they must take precautions to protect themselves from these exposures.
Conclusion
If you are interested in becoming a sterile processing technician, there are several steps you will need to take. First, you will need to complete a formal education and training program. You will also need to possess certain personal qualities that will help you succeed in this field, such as good communication skills and attention to detail. Once you have completed your education and training program and obtained the necessary skills and qualifications, you will be able to begin your career as a sterile processing technician!



Information very important